Wireless chargers have revolutionized the way we power up our devices, but have you ever wondered how they actually work? Without the need for any messy cables or plugs, these chargers use a fascinating technology known as electromagnetic induction. By generating a magnetic field, they are able to transfer electrical energy from the charger to your device, effortlessly powering it up. But it doesn’t stop there. Through intricate coil configurations and innovative design, wireless chargers have also overcome distance limitations, allowing you to charge your devices from a greater range. And with different charging standards, compatibility is no longer a conundrum. The future of wireless charging technology holds endless possibilities and exciting prospects. Get ready to dive into the captivating world of wireless chargers and discover the science behind this remarkable invention.
Magnetic field generation: The foundation of wireless charging technology
How do wireless chargers work? It all starts with the generation of a magnetic field. Think of it as the workhorse of wireless charging technology. Without the magnetic field, the whole system would come to a screeching halt. So, how is this magnetic field created?
The essentials of electromagnetism
To understand the generation of the magnetic field, we need to delve into the world of electromagnetism. Remember playing with magnets as a kid? You probably noticed that they exert a force on each other. Well, that force is created by the magnetic field surrounding the magnets. In a wireless charging system, we replicate this principle using electromagnets.
Electromagnets in wireless charging
So, how do we create electromagnets in a wireless charger? It’s all about the flow of electricity. When an electric current flows through a wire, it generates a magnetic field around it. This magnetic field is the secret ingredient that allows wireless chargers to work their magic.
[amazon bestseller=”wireless chargers” items=”10″]
Exploring electromagnetic induction: The key principle behind wireless chargers
Now that we have our magnetic field, we need to understand how it interacts with our electronic devices. This is where electromagnetic induction comes into play. It’s the principle that enables wireless chargers to transfer electrical energy without the need for physical contact.
The dance between magnetic fields
Imagine a captivating dance between two magnetic fields. When an alternating current is supplied to the transmitter coil in a wireless charger, it generates a changing magnetic field. This changing magnetic field then induces a voltage in the receiver coil of your device. It’s like a musical duet where the magnetic fields harmonize to transfer energy.
Maximizing energy transfer efficiency
But here’s the catch: not all of the energy from the magnetic field is successfully transferred to your device. Some of it gets lost along the way. To overcome this challenge, wireless chargers are designed to optimize energy transfer efficiency. By fine-tuning the design of the coils and minimizing energy losses, engineers strive to ensure the maximum amount of energy is transmitted to your device.
From charger to device: Understanding the transfer of electrical energy
Now that we have established the foundation and principles behind wireless charging, let’s explore how the electrical energy actually travels from the charger to your device.
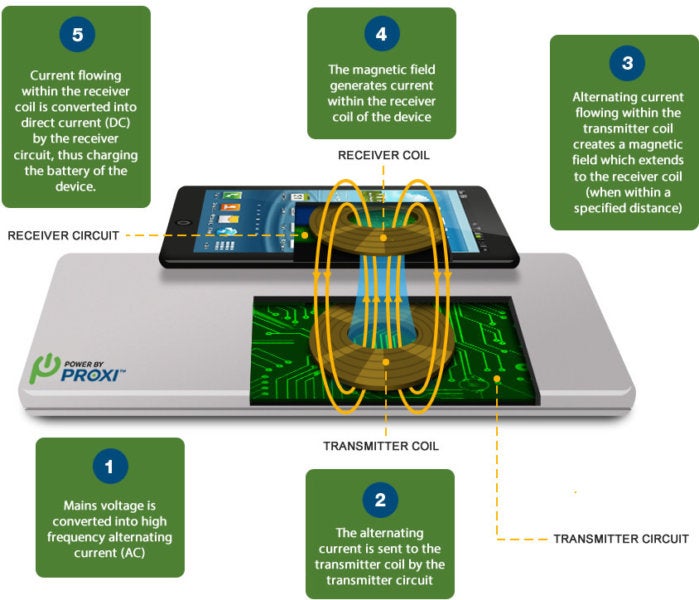
Converting AC to DC
When an alternating current is supplied to the transmitter coil, it creates an alternating magnetic field. This alternating magnetic field induces an alternating voltage in the receiver coil of your device. However, your device requires direct current (DC) to operate. So, before it can be used, the alternating current needs to be converted into direct current.
The role of rectification
To achieve this conversion, a component called a rectifier is used. The rectifier converts the alternating current into direct current by only allowing current to flow in one direction. This ensures that the energy transferred from the wireless charger is in a form that your device can utilize.
Coil configuration: Unraveling the mysteries of transmitter and receiver coils
Finally, let’s take a closer look at the coils that are at the heart of a wireless charging system. These coils play a crucial role in generating and receiving the magnetic fields necessary for wireless charging.

The transmitter coil
The transmitter coil, as the name suggests, is responsible for generating the magnetic field. It is typically housed within the wireless charger and carries the alternating current that creates the changing magnetic field. The size, shape, and number of turns in the transmitter coil are carefully designed to optimize the efficiency and range of the magnetic field generated.
The receiver coil
On the receiving end, we have the receiver coil, which is integrated into your device. This coil acts as an antenna, capturing the changing magnetic field generated by the transmitter coil. The induced voltage in the receiver coil is then used to charge your device’s battery or power its operations. Just like the transmitter coil, the configuration of the receiver coil is critical in ensuring efficient energy transfer.
In conclusion, wireless chargers work by generating a magnetic field using electromagnets, which is then utilized through electromagnetic induction to transfer energy from the charger to the device. The coils in the transmitter and receiver play essential roles in generating and receiving the magnetic fields, while the electrical current is converted from alternating to direct current for the device’s use. Understanding these concepts gives us a glimpse into the science behind the conveniences of wireless charging technology.
Magnetic field generation: The foundation of wireless charging technology
When it comes to wireless charging, the first thing that comes to mind is the convenience of not having to deal with tangled wires. But have you ever wondered how exactly these chargers work? Well, it all starts with the generation of a magnetic field.

Magnetic fields – the invisible force behind wireless charging
At the heart of wireless charging technology lies the concept of magnetic fields. These are invisible forces that surround magnets or electric currents, extending into the space around them. Just like how a pebble creates ripples when it falls into a calm pond, an electric current creates a magnetic field when it flows through a wire.
Coils – the secret conductors of magnetic fields
To generate a magnetic field in wireless chargers, coils play a vital role. Coils are nothing but tightly wound conductive wires that can efficiently carry electric currents. When an electric current passes through a coil, it creates a magnetic field that is strong enough to induce a charge in another nearby coil.
Exploring electromagnetic induction: The key principle behind wireless chargers
Now that we understand how magnetic fields are generated, let’s dive into the fascinating principle behind wireless chargers – electromagnetic induction.
Electromagnetic induction – the magic behind wireless charging
Electromagnetic induction is the process by which a changing magnetic field creates an electric current. When a wireless charger is plugged into a power source, it converts the electrical energy into an oscillating magnetic field.
Transmitter and receiver coils – the key players in electromagnetic induction
To make wireless charging possible, there are two essential components: the transmitter coil and the receiver coil. The transmitter coil, present in the charging pad, generates the oscillating magnetic field. On the other hand, the receiver coil, integrated into the receiving device, picks up that magnetic field and converts it back into electrical energy.
From charger to device: Understanding the transfer of electrical energy
Now that we know how the magnetic fields are created and electromagnetic induction works, let’s explore how the electrical energy is transferred from the wireless charger to the device that needs to be charged.
The power of resonance: Efficient energy transfer
Wireless chargers often use the power of resonance to transfer electrical energy. Resonance occurs when two objects vibrate at the same frequency. In the case of wireless chargers, the transmitter and receiver coils are designed to have the same resonant frequency. This allows for efficient energy transfer, minimizing losses and maximizing the amount of power delivered to the device.
Powering up: Charging your device wirelessly
When you place your device on a wireless charging pad, the receiver coil within the device picks up the oscillating magnetic field created by the transmitter coil. This induces an electric current in the receiver coil, which is then used to charge the device’s battery. It’s like a dance between the coils – one waltzes with electricity, while the other follows its lead.
Coil configuration: Unraveling the mysteries of transmitter and receiver coils
In the world of wireless chargers, there’s more to coil configuration than meets the eye. Let’s uncover the secrets behind how transmitter and receiver coils are designed for optimal wireless charging.
The importance of alignment: Getting in the right position
To ensure efficient charging, it’s crucial to align the transmitter and receiver coils properly. This alignment ensures that the magnetic field generated by the transmitter coil is picked up by the receiver coil, maximizing the transfer of electrical energy. Imagine trying to catch a ball with your eyes closed – it’s much easier when you’re looking in the right direction!
A delicate balance: The trade-off between distance and efficiency
Wireless charging technology often faces a trade-off between charging distance and efficiency. As the distance between the transmitter and receiver coils increases, the strength of the magnetic field diminishes, resulting in lower efficiency. Manufacturers must strike a delicate balance, designing wireless chargers that provide both convenience and charging speed.
So, the next time you place your device on a wireless charger, remember the invisible dance between magnetic fields, the power of electromagnetic induction, and the careful alignment of coils. Wireless charging may seem like magic, but it’s actually a fascinating interplay of science and technology, bringing us one step closer to a wire-free world.
Conclusion
Wireless chargers have revolutionized the way we power our devices, providing a convenient and tangle-free solution. Understanding how do wireless chargers work reveals the intricate processes that enable this technology. By generating magnetic fields through electromagnetic induction and transferring electrical energy from the charger to the device, wireless chargers offer a seamless charging experience. The configuration of transmitter and receiver coils, along with optimizing power output and efficiency, further enhance the performance. Overcoming distance limitations and navigating different charging standards have brought about advancements in wireless charging range and compatibility. As we explore the future of wireless charging technology, we can envision a world where power is effortlessly transmitted, eliminating the reliance on cumbersome cords. The possibilities are endless, and the future of wireless charging is bright.

Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do wireless chargers work?
Wireless chargers use a process called electromagnetic induction to transfer energy from the charger to your device. The charger creates a magnetic field that energizes a coil inside your phone or other compatible device. This magnetic field generates an electrical current in the coil, which charges your device’s battery.
2. Are wireless chargers compatible with all devices?
Wireless chargers are not compatible with all devices. Most modern smartphones, including iPhone 8 and newer models, and many Android devices, support wireless charging. However, older devices or those without built-in wireless charging capabilities may require an additional accessory, such as a wireless charging receiver or a specific case, to enable wireless charging.
3. Is wireless charging as fast as wired charging?
Wireless charging is generally slower than wired charging. The charging speed of wireless chargers can vary depending on the device and charger you’re using. In most cases, wireless charging tends to be slightly slower compared to traditional wired charging. However, advancements in technology are constantly improving wireless charging speeds.

4. Can I still use my phone while it’s charging wirelessly?
Yes, you can definitely use your phone while it’s charging wirelessly. Wireless chargers allow you to use your device normally while it continues to charge. You can make calls, send messages, browse the internet, or even watch videos while your phone sits on the wireless charger.
5. Are wireless chargers safe for daily use?
Yes, wireless chargers are safe for daily use. They follow industry standards and regulations to ensure your safety. However, it’s important to buy wireless chargers from reputable manufacturers to avoid any potential safety risks. It’s also worth noting that wireless charging generates heat, but modern chargers have built-in safety mechanisms to prevent overheating and protect your device.











